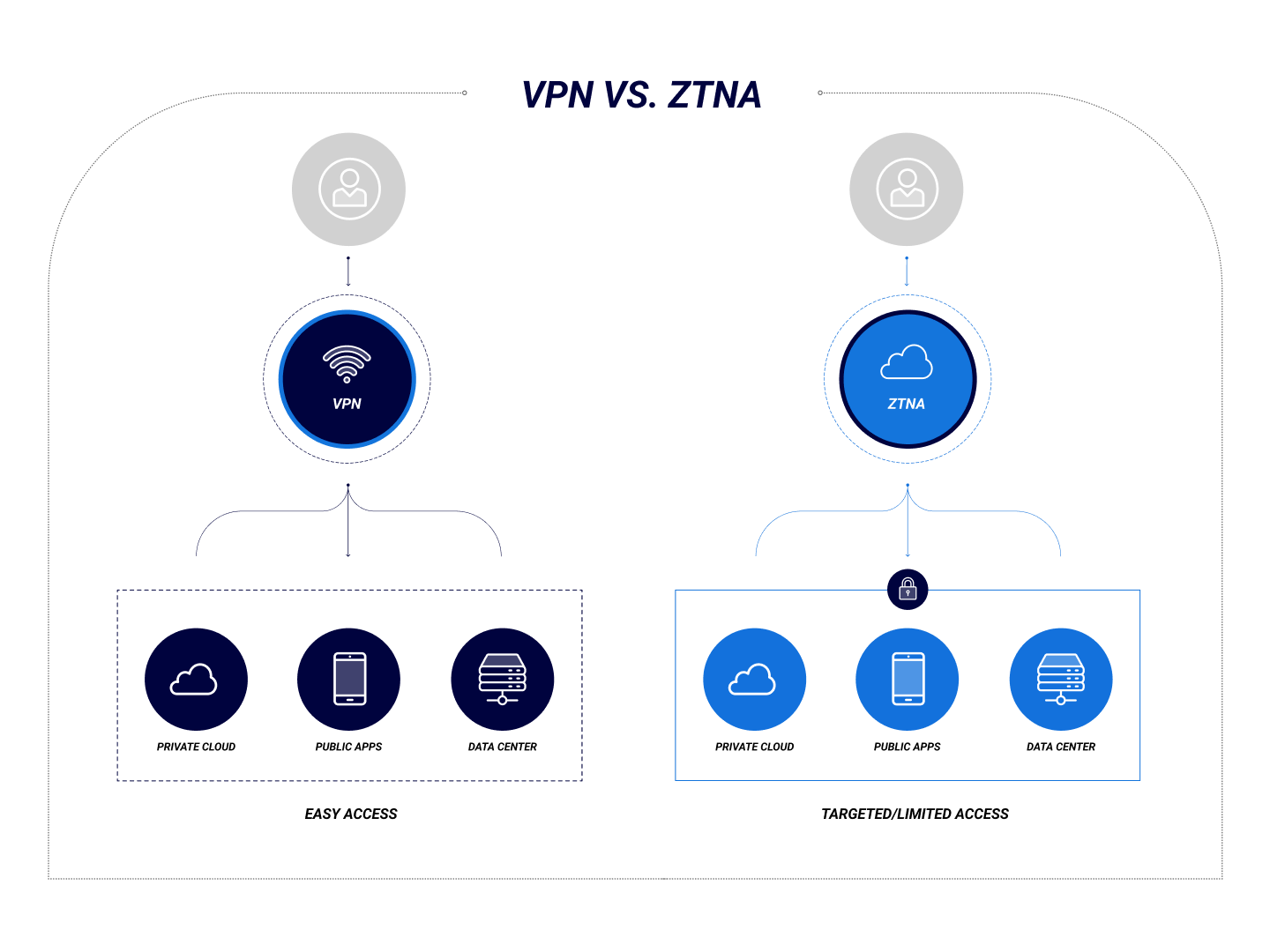
VPNs were introduced more than 30 years ago to grant access to configured endpoints on local area networks (LANs) over the internet. Once a user is granted access, they can access anything on the network.
ZTNA, on the other hand, provides remote access to individual applications or services based on granular access control policies. It implements the security principles of Zero Trust and continuously monitors user activity during the user's session, demanding re-authentication periodically or when the connection is idle for some time.
What Is VPN?
An enterprise VPN is designed to provide secure remote access to LAN endpoints. The technology is commonly used for remote desktop access to an employee's office computer. VPN uses a point-to-point (P2P) connection or encrypted "tunnel" to protect an internal endpoint's IP address from being exposed publicly while still allowing a direct connection.
Common VPN Protocols
- IPSec/IKEv2
- IPSec/L2TP
- OpenVPN
- Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) enables secure remote access to individual internal applications and includes context-based access control technologies. ZTNA provides a secure authentication process and limits the tools available to an attacker who has compromised a remote access service.
ZTNA provides access via an access broker security agent. The agent not only verifies user identity, context, and policy adherence but also requires periodic re-authentication for extra security. ZTNA applies an adaptive trust model, where trust is never implicit, and access is granted on a least-privilege basis defined by granular policies. A ZTNA access broker can also assess the connection context, including device security posture and client geolocation, and may require multi-factor or biometric authentication.
How Is ZTNA Different from VPN?
Unlike VPNs, which provide direct tunneled access to an endpoint on a corporate LAN, ZTNA provides access only to explicitly authorized applications and services. The primary goal of ZTNA is not to prevent exposing the internal IP address of a particular resource but to provide granular access control to services with continuous monitoring of connection behavior and context-aware re-authentication aligned with Zero Trust principles.
Although ZTNA technologies do not currently allow a complete bridging of two separate corporate LANs into a WAN, it does allow applications and resources to be Cloud-hosted, allowing remote connections from anywhere.
What's Better: VPN or ZTNA?
VPN connections are "all or nothing," providing full access to an internal endpoint and all its built-in tools, which incurs risk. VPN also lacks strong authentication controls and visibility for monitoring user behavior at the endpoints.
ZTNA is better suited than VPN for securing access to an organization's internal resources by allowing granular control over which applications can be accessed and by implementing Zero Trust-based authentication technologies. ZTNA continuously monitors user activity during and after connecting without exposing the internal network.
Between the growing complexity of supply chains, the proliferation of IoT devices, and the increased focus on remote work, the network security challenges faced by modern businesses seem almost insurmountable. Administrators need a way to support distributed work, yet they also cannot afford to put critical assets at risk. Complex and resource-heavy VPNs are ill-suited for this task.
CylanceGATEWAY™ is a cloud-native ZTNA solution designed to support scalable, outbound-only access to business-critical applications and services. Its multi-tenant architecture is designed with digital transformation and distributed work in mind, while its powerful artificial intelligence simultaneously augments your business’s security posture and simplifies the configuration and management of granular, dynamic policies and access controls.