What Is the Follina Vulnerability?
Follina is a high-severity vulnerability discovered in the Microsoft Office suite of products that is easy to exploit for remote code execution (RCE) attacks. Microsoft has released security updates for all products affected by Follina; however, many unpatched versions of Microsoft Office products are still vulnerable. NIST assigned Follina the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposure (CVE) number CVE-2022-30190 for tracking purposes.
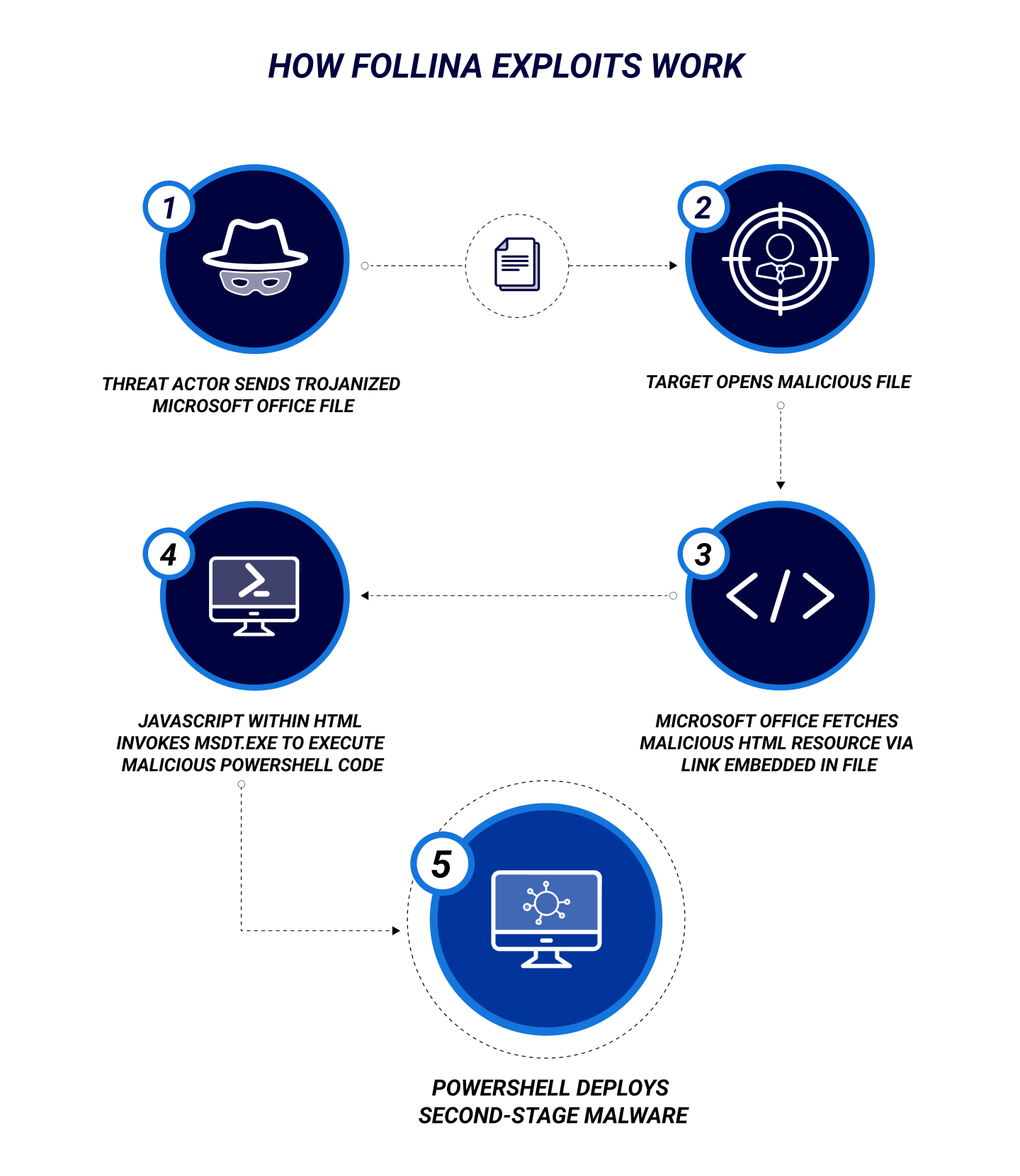
Threat actors exploit Follina through phishing campaigns, directing targeted users to open an Office document containing a Web-link to an attacker-controlled online resource. The Office application automatically fetches these embedded links, and their content is specially crafted to invoke a Microsoft service known as the “Microsoft Support Diagnostic Tool” (MSDT) protocol. MSDT (msdt.exe) is typically used to collect information and report system crashes to Microsoft support, but an MSDT protocol link can also be used to force the execution of attacker-supplied PowerShell commands—without additional user interaction.
An exploit of the Follina flaw may require a user to open a Microsoft Office document such as a Word .docx file containing malware delivered via email or other online communication channels—or even via a USB device. But it may not require a click: if the malicious file is in .rtf format, for instance, the code could run via the Preview Tab in Explorer, without the user ever having opened the file. Either way, the malware payload is activated through MSDT.
Follina was first publicly disclosed as a zero-day vulnerability in a tweet by @nas_sec on May 27, 2022; the first recorded malware sample leveraging Follina in the wild was observed by security researchers on April 7, 2022. However, the Follina flaw had likely been exploited for some time before its discovery. Since the first recorded sighting, cybersecurity researchers have identified a sharp increase in phishing campaigns with attachments leveraging Follina; the vulnerability will continue to be exploited in phishing attacks against unpatched systems.
Who Is Affected by Follina?
Follina affects various Microsoft products, including Office suite 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021 applications, and some versions of Office included with a Microsoft 365 license installed on Windows desktop PCs and servers since 2007. Due to Microsoft Office’s status as the most popular business productivity software in the world, the expected impact is high and global in scope, affecting most personal and corporate computing environments. Office applications are vulnerable to Follina even with Office VBA macros turned off, further increasing the scope of potential victims.
Follina has been observed in the wild being aggressively exploited by state-backed advanced persistent threat (APT) actors, including APT TA570 (Qbot affiliate) in phishing campaigns to install Qbot malware on victim hosts and in phishing attacks against US and EU government agencies.
Because Follina is simple to exploit, even a novice attacker could take remote control of systems, and publicly available proofs-of-concept make accessing or creating Follina malware easy.
How Bad is Follina?
Follina is a high-severity security vulnerability considered trivial to exploit and can lead to remote code execution (RCE). Follina does require user interaction to achieve payload execution, but this can be achieved by tricking a victim into opening a malicious document or link delivered via email or social media. Once a document containing Follina malware has been opened, RCE with the system permissions level of the compromised Office application is possible.
Once the attacker has RCE at user-level permissions, they can exploit any user applications, destroy or ransom documents, or redirect their attack tactic to escalate privileges, seeking to obtain complete system admin privileges and pivot to compromise more valuable targets within the victim’s network environment.
Microsoft initially published a temporary workaround for Follina that prevents a successful attack via known vectors. The first officially prescribed fix was to disable the MSDT protocol in the Windows operating system. Since then, Microsoft has released Windows updates that prevent the MSDT protocol from automatically executing attacker-supplied code. But organizations should also employ user awareness training programs to better educate staff about how to identify phishing attacks.
Follina is not the first recently disclosed high-severity vulnerability in popular software that takes advantage of a “feature” such as MSDT. In late 2021, the Log4Shell vulnerability was disclosed, which leverages a feature in the Apache Software Foundation’s Log4j logging library, giving attackers RCE. Because new software vulnerabilities are disclosed regularly and are unpredictable—software patches sometimes take weeks for vendors to develop; traditional endpoint security products do not have signatures to detect new malware—advanced cybersecurity products are the best way to maintain strong security assurances against zero-day attacks.
FAQ
What is the Follina vulnerability?
Follina is a high-severity vulnerability discovered in the Microsoft Office suite of products that is considered trivial to exploit and can lead to remote code execution by an attacker. Follina affects Microsoft Office 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021 (and some versions of Office included with a Microsoft 365 license) installed on all Windows desktop and server versions since 2007.
Follina payloads can be delivered remotely through the opening of an infected document; malware executed via Follina can perform a wide range of malicious activity on the victim’s device, from stealing banking credentials to locking up systems and demanding a ransom to exfiltrating sensitive information, such as personal, medical, or financial data.
How do I protect against Follina?
The first officially available remediation was to disable the MSDT protocol altogether, but Microsoft has since released updates to Windows that will prevent the MSDT protocol from automatically executing attacker-supplied code. Implementing the initial workaround fix and installing Windows updates is highly recommended.
Learn More